| Complex formation with starch |
| Hydrophilic sugar esters (high HLB values) are effective as a quality improver in foods consisting mainly of wheat flour. Sugar esters combine with starch in a form where the helical structure of the starch envelops the fatty acid group of sugar ester. When sugar esters are combined with starch, especially amylose, the quality of the starch product is remarkably improved.
(1) Dough of bread, biscuit, cookies, etc. (2) The complex of sugar esters and amylose after elution from starch granules lowers the rate of recrystallization with time and prevents starch granules from being concreted. In other words it is effective as a softener in bread or cake.
(3) Sugar esters control the swelling of starch particles, and are utilized to inhibit a 'gummy layer' or 'cheesy layer' in cake and
improve the crumb.
(4) Sucrose monopalmitate promotes the role of natural glycolipid in wheat flour. |
|
<<Figs.>> Influence of sugar ester chain length and HLB values on the gelatinization of potato starch in a Brabender amylograph. (potato starch:19g,sugar ester:1g,water:450g)
<A> chair length 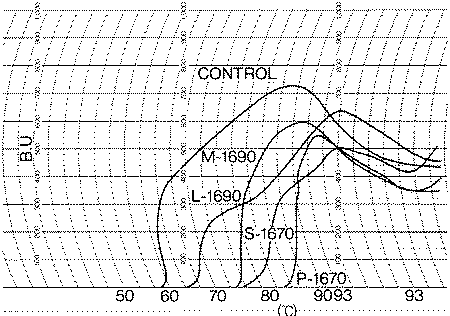
<B> HLB values  |
